Life Cycle of a Parrot
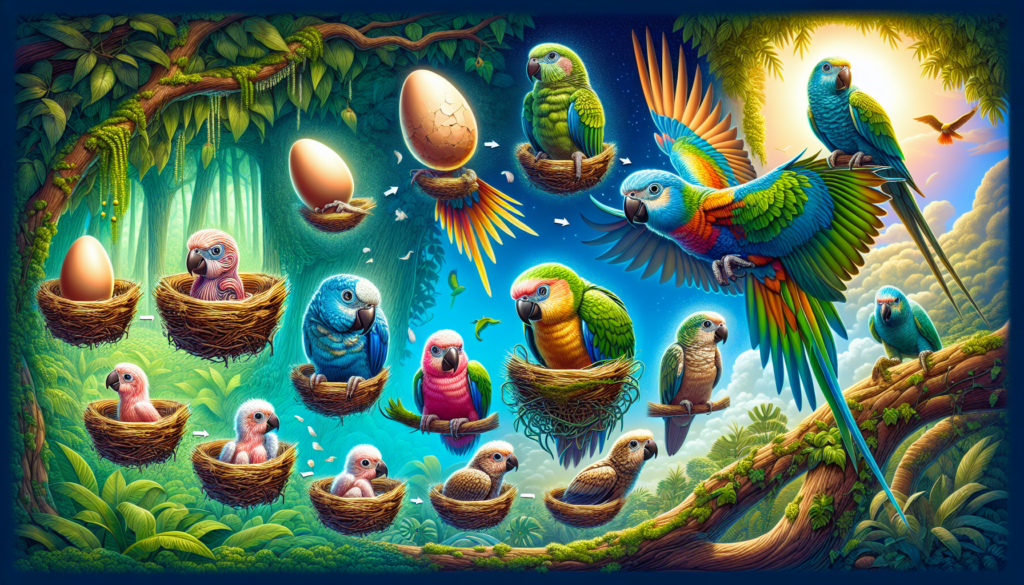

Hey everyone, welcome back to Feathered Mates! Today, I will talk about the Life Cycle of a Parrot. Parrots are very Intelligent birds, because of which people have been breeding parrots for thousands of years. Parrots are well known for their ability to mimic human speech and other sounds.
In this Article, We will learn about the parrot life cycle. We will focus on growth, development, learning and socialization of parrots from the egg and hatching stages of their life cycle to adulthood and mating.
Life Cycle of a Parrot-Egg and Hatching Stage
Parrots usually lay two to eight eggs per clutch. The number of eggs laid may vary depending on the species. For example, African grey parrots usually lay three to four eggs per clutch. Their eggs are hatched by both parents which may incubate for 18 to 30 days. Maintaining proper temperature and humidity during this critical period is crucial for hatching.
Temperature:
The ideal temperature for parrot eggs is 98.7 to 100 degrees Fahrenheit. (98.7-99.3°F) works well for large eggs but (99.3-100°F) is required for small eggs.
Humidity:
All successful incubation requires a humidity level of 38 to 52 percent. Large eggs do best at 38 to 45 % humidity. But small eggs require 46 to 52 % humidity.
Egg turning:
Changing eggs four to eight times a day is considered sufficient for proper development of parrots.
Once the incubation period is over, the eggs begin to hatch. The first sign of impending is egg “dropping” which usually occurs about three days before hatching. Hatchlings are born blind featherless, and helpless, requiring extensive parental care. Parents feed the chicks a diet of seeds, fruit and insects. In the first few weeks of life, chicks begin to develop feathers and their eyes open. Baby birds stay with their parents for several months after hatching and learn skills necessary for survival.
Juvenile Stage – Life Period Of Parrot
The adolescent phase of parrots begins after weaning. During this stage the parrot grows and develops by observing and imitating parents and peers, acquiring essential survival skills and social skills. Juvenile parrots go through their own version of adolescence and adulthood establishing their unique personalities and finding their place in the larger group. As they mature between the ages of one and four, their personalities may change, sometimes showing signs of aggression especially during mating season.
To support the juvenile parrot’s growth and development, it is recommended to:
- Keep feeders full of nutritious mixes such as lyric fine tunes, no waste mixes that provide easy access to food and energy.
- Provide an environment with toys, perches, and opportunities for social interaction to encourage learning and socialization.
- Monitor the parrots behavior and critical needs by contacting a veterinarian.
Adolescence – Learning and Socialization
Adolescence is a crucial stage in a parrot’s life, where they learn essential social behaviors and establish their unique personalities. During this period, parrots may become more assertive or dominant, testing their social status within their flock or human family. Proper socialization is key to preventing behavioral problems in adulthood.
Interaction with other parrots or birds can help adolescent parrots learn appropriate social behaviors, while human interaction helps them become comfortable with their caregivers. Training and positive reinforcement can be used to guide their behavior and strengthen the bond between the parrot and its caregiver. Consistency in training and care is essential, as adolescent parrots can be sensitive to changes in routine.
Providing a variety of toys and activities can help keep adolescent parrots mentally stimulated and prevent boredom. Supervision is necessary during this period, as they may engage in destructive or unwanted behaviors. Patience, consistency, and calmness are key during the puberal stage, which can occur between 2-4 years for medium parrots and 3-6 years for large ones. The end of puberty reveals a more tolerant, peaceful, and mature parrot.
Adulthood and Mating
Parrots are social birds that live in flocks and are known for their monogamous mating habits, meaning they mate with one partner for life. They reach sexual maturity between one and four years of age, depending on the species. During the mating season, which typically occurs in the spring and summer months, parrots engage in elaborate courtship displays, including vocalizations, parades, and gift-giving.
Once a pair has chosen a mate, they will typically stay together for life, forming strong pair bonds. Some species have been observed to display signs of grief and mourning when a mate dies. Adult parrots are capable of reproducing and starting their own families], with lifespans varying greatly depending on the species, ranging from about 15 to 80 years in the wild.
During the mating season, pet parrots may exhibit hormonal behavior, such as aggression, lunging, protecting food or cage, and even mating dances. Hormonal triggers can lead to protective and aggressive behavior, especially around the cage. To minimize hormonal behavior, owners can take certain measures, such as:
- Removing potential nesting material from the cage
- Feeding a balanced diet and tracking weight
- Maintaining a consistent sleep cycle
- Handling and socializing the parrot regularly.
Life Cycle of a Parrot is a fascinating journey, from the delicate incubation period of their eggs to the growth and development of the juvenile stage. As they progress through adolescence, parrots learn essential social skills and establish their unique personalities. Upon reaching adulthood, these intelligent birds form strong, lifelong bonds with their chosen mates and may even start their own families.
Click here to know How Long Do Parrots Live?
It can be said that birds are very peaceful creatures and they always fascinate us with their behavior. So, As a responsible bird owner, acquiring the necessary knowledge about birds is of course very important. Every bird owner should understand and review accurate information about birds and guide birds properly. Hope we have helped you enough on how to choose the best Duck Food. Stay with us to learn about the right bird selection, Birds care, birds nests and all things related to birds. May the relationship between you and your pet become stronger.
Frequently Asked Questions
The life cycle of a parrot includes several key phases, starting with Parrot Imprinting, where a chick forms a deep bond with its parent after first opening its eyes around two weeks old. This is followed by the Fledgling stage, the practice of Clipping a Parrot Chick’s Wings, Weaning, the Juvenile stage, reaching Mating Age, and finally, the Adult stage. The life span of parrots is also a notable aspect of their life cycle.
Certainly, the life cycle of a bird is typically divided into seven stages: 1) The Egg, 2) The Hatching, 3) The Nestling, 4) The Fledgling, 5) The Juvenile, 6) The Sub Adult, and 7) The Adult.
The life cycle of a bird progresses through seven stages. It begins with an egg laid in a nest. After hatching, the bird enters the second stage as a chick. As it grows, it goes through the nestling stage, followed by further development until it becomes a mature bird.
In their natural habitat, parrots are diurnal, meaning they are active during the daytime. They typically wake up at sunrise and remain active for about 12 hours. After sunset, they sleep for the remaining 12 hours of the day.